Understanding Decentralized Applications (DApps): The Future of Software Development

Introduction to DApps
Decentralized applications, commonly referred to as DApps, represent a substantial shift in the way software is developed and deployed. Unlike traditional applications that operate on centralized servers, DApps function on a distributed network, typically utilizing blockchain technology. This decentralized architecture empowers developers and users, enhancing security, privacy, and censorship resistance.
Table of Contents
At their core, Decentralized applications are built on principles that prioritize decentralization, transparency, and immutability. They leverage smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with predetermined rules encoded within the blockchain. These smart contracts facilitate operations without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. As a result, DApps can operate autonomously, aligning with users’ interests rather than being dictated by a single governing entity.
The relevance of blockchain technology in the operation of Decentralized applications cannot be understated. Blockchain serves as the foundation for these applications, ensuring that all transactions are recorded in a tamper-proof ledger. This not only enhances the integrity of the data but also establishes trust among users, as actions taken within the DApp cannot be altered retrospectively. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain diminishes the single points of failure inherent in traditional applications, making DApps more resilient against attacks and downtime.
In contrast to conventional applications that rely on proprietary servers and software, Decentralized applications foster an ecosystem where users can interact directly with each other. This not only democratizes access to resources but also incentivizes user engagement through tokenomics, where users can earn rewards for their participation. Thus, DApps are not only a technological advancement but also a paradigm shift in how software can be developed, governed, and utilized across various industries.
Key Characteristics of DApps
Decentralized applications, commonly referred to as DApps, possess several key characteristics that set them apart from traditional software applications. Understanding these characteristics is essential for grasping how DApps function and their potential impact on various industries.
One of the defining features of Decentralized applications is decentralization. Unlike conventional applications that typically rely on a central server, DApps operate on a distributed network of nodes. This decentralization eliminates the risks associated with centralized control, such as single points of failure. For instance, a DApp deployed on the Ethereum blockchain leverages the collective power of numerous nodes, making it more resilient against outages and censorship.
Another critical aspect of DApps is their open-source nature. The source code of a DApp is publicly accessible, allowing developers to inspect, modify, and enhance it. This characteristic fosters innovation and collaboration within the developer community. A notable example of this can be seen in DApps like Uniswap, where developers can contribute to the protocol or create their own projects based on the existing open-source code.
Token-based economics further distinguishes DApps from traditional applications. Many Decentralized applications incorporate cryptocurrencies or tokens, enabling users to transact within the platform as well as rewarding contributors. An example would be the use of governance tokens in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, where token holders possess the ability to vote on crucial protocol decisions, effectively influencing the future trajectory of the DApp.
Finally, DApps operate on peer-to-peer networks, facilitating direct interactions between users without intermediaries. This characteristic not only enhances trust among participants but also reduces transaction costs. Platforms such as Filecoin exemplify this peer-to-peer model, enabling users to buy and sell storage directly, thereby promoting a more efficient digital economy.
Advantages of Decentralized Applications
Decentralized applications (DApps) have emerged as a pivotal innovation in the realm of software development, offering a myriad of benefits that enhance user experience and security. One of the primary advantages of DApps is enhanced security. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized servers, DApps distribute data across a network of nodes. This decentralized architecture significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, as there is no single point of failure. Consequently, users can engage with these applications with greater confidence in the protection of their sensitive information.
In addition to security, Decentralized applications also promote increased user privacy. With traditional applications, user data is often stored in centralized databases, which can be susceptible to harvesting and misuse. DApps, on the other hand, prioritize user control over their data. By employing cryptographic techniques and decentralized storage, DApps ensure that users maintain ownership of their personal information, effectively mitigating privacy concerns associated with conventional software.
Censorship resistance is another notable benefit of DApps. By leveraging blockchain technology and decentralized networks, these applications resist attempts at censorship by authorities or malicious entities. This ensures that users can access the applications freely, fostering a more open and democratic digital landscape. A prominent example is Ethereum-based DApps, which allow developers to create a plethora of applications across various domains, ranging from finance to social networking, without the fear of interference.
Furthermore, Decentralized applications reduce dependence on centralized authorities, which can be particularly advantageous in regions with unstable governance or restrictive regulations. This independence not only empowers users but also fosters innovation and competition in the software development sphere. Overall, the advantages of DApps extend beyond security and privacy; they enable a transformative shift towards a more user-centric and resilient software ecosystem.
Challenges and Limitations of DApps
Decentralized applications, commonly known as dApps, have gained significant attention, yet they are not without their challenges and limitations. One prominent issue is scalability. Traditional applications can handle thousands of transactions per second, while many dApps built on blockchain networks often struggle to accommodate a high volume of users. This scalability challenge emerges from the inherent design of blockchain technology, which prioritizes decentralization and security over speed. As user adoption increases, the networks can face congestion, leading to slower transaction speeds and diminished user satisfaction.
Another critical challenge facing dApps is the often high transaction costs associated with operating on blockchain platforms. Users may encounter elevated fees, particularly during peak usage periods or on networks with limited capacity. These costs can act as a deterrent for potential users compared to conventional applications that typically have lower or no direct transaction costs. High fees not only impact user experience but also hinder the broader adoption of dApps across diverse industries.
The complexity of the user experience is yet another hurdle. Many dApps require users to possess a certain level of technical knowledge, such as understanding cryptocurrency wallets and navigating blockchain interfaces. This complexity can alienate non-technical users and restrict the widespread use of these applications. Additionally, the competing standards and protocols across various blockchain platforms can make it challenging for developers to create seamless and user-friendly experiences.
These challenges significantly affect the adoption and growth of dApps across various sectors. As developers and stakeholders work to address these limitations, the evolution of dApps will play a crucial role in determining their future impact on software development and digital interactions.
Popular Platforms for DApp Development
The development of decentralized applications (DApps) has gained significant traction, with several platforms emerging as the preferred environments for developers. Among them, Ethereum stands out as the pioneer of DApp innovation. Its robust smart contract capabilities, expansive developer community, and extensive resources have made it a go-to choice for new applications. Furthermore, Ethereum’s strong security protocols contribute to its reputation as a reliable platform, although it does face challenges, such as scalability and high transaction fees, particularly during peak usage periods.
Another notable platform is Polkadot, designed to enhance interoperability between different blockchains. Its unique architecture allows DApps to communicate across various blockchains, which is advantageous for developers looking to create applications that leverage multiple networks. Polkadot’s scalability is a key strength, enabling it to support numerous DApps simultaneously. However, its relatively newer presence in the market means that the ecosystem is still growing in terms of available tools and resources.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) has also gained popularity due to its low transaction fees and fast processing times, appealing to developers who are looking to create efficient DApps. BSC is compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to migrate their applications between the two platforms with ease. However, concerns regarding centralization and security are critical considerations for developers when choosing BSC for their DApp projects.
Other platforms worth mentioning include Cardano, known for its rigorous approach to scalability and sustainability, and Solana, celebrated for its high throughput. Each of these platforms offers unique features and advantages, empowering developers to select the right environment based on their project requirements and objectives. Ultimately, the choice of platform will significantly influence the development process and success of the DApps being created.
Use Cases of DApps Across Industries
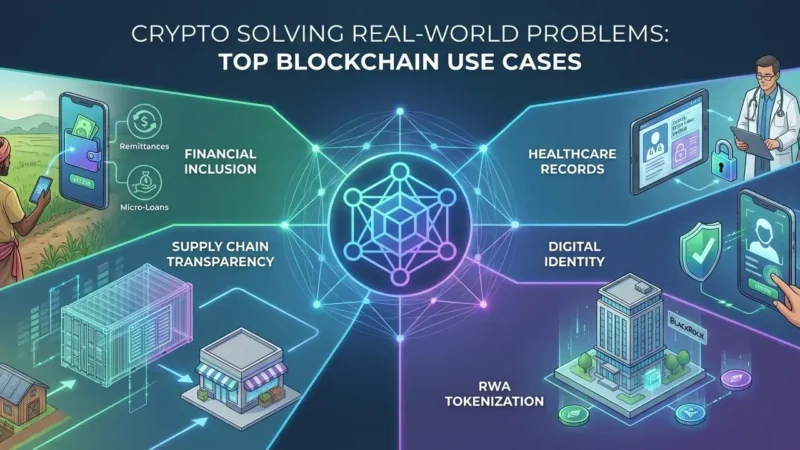
Decentralized applications (DApps) are increasingly recognized for their potential to transform traditional business models across various industries. One of the most notable areas of impact is finance, often referred to as decentralized finance (DeFi). In DeFi, DApps enable users to engage in financial transactions without intermediaries, relying instead on blockchain technology. This innovation includes services like lending, borrowing, and trading, which operate in a transparent and tamper-proof environment, significantly reducing fees and increasing accessibility for individuals worldwide.
In the gaming industry, DApps are creating new paradigms for ownership and monetization. Players can truly own in-game assets through non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which can be traded or sold on decentralized marketplaces. This shift empowers players, providing them with tangible value from their investments in time and resources. Furthermore, DApps facilitate peer-to-peer gaming experiences, eliminating centralized control and fostering a more collaborative online gaming culture.
Healthcare is another sector ripe for the adoption of DApps. By utilizing blockchain technology, patient records can be securely shared between healthcare providers while maintaining privacy and data integrity. Smart contracts can automate processes such as insurance claims, streamlining administration and reducing fraud. This transparency can lead to improved patient outcomes and enhanced trust among stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.
Supply chain management also benefits significantly from DApps. By providing end-to-end visibility, organizations can track products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. DApps can log each transaction on the blockchain, allowing stakeholders to verify the journey of goods and comply with regulations more efficiently. This increasing transparency can lead to optimized operations, as companies can identify inefficiencies and respond to disruptions rapidly.
Overall, while the concept of DApps is still evolving, their diverse applications across industries indicate a promising future where traditional processes can be reimagined and enhanced through decentralized technology.
Developing Your Own DApp
Creating a decentralized application (DApp) involves a series of carefully planned steps that ensure functionality and security within a blockchain ecosystem. The first crucial step is selecting the appropriate platform. Several blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polkadot, provide diverse options based on scalability, transaction speed, and community support. It is essential to consider factors such as the target audience, existing infrastructure, and the specific use case of the DApp when deciding on a platform.
Once the platform is chosen, the development of smart contracts follows. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They are the backbone of any DApp, enabling interactions without intermediaries. Developers typically use Solidity or Vyper for Ethereum-based projects, and these languages allow for the creation of complex functionalities while ensuring security protocols are adequately addressed. Rigorous testing is necessary to prevent vulnerabilities, given the immutable nature of blockchain transactions.
Following the smart contract stage, developers should focus on creating an engaging user interface (UI). A well-designed UI enhances user experience and drives adoption. Frameworks like React or Angular can be used to build web-based front ends, while libraries such as web3.js or ethers.js facilitate seamless interaction between the frontend and the smart contracts deployed on the blockchain.
Finally, the DApp must be deployed on the chosen blockchain. This process involves publishing the smart contracts to the network, which can be done using tools like Truffle or Hardhat, and subsequently configuring the user interface to connect with these contracts. Post-deployment, continuous monitoring and updates will help improve the application’s performance and security. With the right tools and a structured approach, developing a robust DApp is achievable.
The Future of DApps
The landscape of decentralized applications (DApps) is poised for significant evolution as technology and user needs advance. One of the most promising trends is the interoperability of various blockchains, which aims to facilitate seamless communication and operation between distinct decentralized networks. This would empower developers to create applications that can utilize multiple blockchains, thus enhancing functionality and user experience. The capacity to interact with different protocols could lead to a more robust ecosystem, where DApps are not confined to a single blockchain but can tap into various technologies for improved scalability and efficiency.
Additionally, advancements in decentralized finance (DeFi) are expected to play a crucial role in the future of DApps. As traditional financial systems become increasingly integrated with blockchain technology, DApps will likely evolve to provide more sophisticated financial services, including automated market making, lending, and insurance services. These advancements will not only democratize access to financial resources but also foster an environment where users can engage in complex financial activities without intermediaries, thereby lowering costs and increasing transparency.
The rise of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) is another significant trend influencing the development of DApps. DAOs offer a revolutionary governance model where decisions are made collectively by stakeholders, often through smart contracts. This could enable DApps to be managed in a more democratic and efficient manner, allowing users to participate actively in the decision-making process. As communities around DAOs grow, they are likely to create an ecosystem of DApps centered on collaboration, shared values, and collective progress.
In conclusion, the future of DApps appears bright, characterized by increasing interoperability, advancements in decentralized finance, and the proliferation of DAOs. As these trends develop, they will reshape the way users interact with technology and transform the overall software development landscape.
Stay informed, read the latest crypto news in real time!
Conclusion
In reviewing the key points discussed, decentralized applications, commonly referred to as dapps, represent a pivotal shift in the software development landscape. Their unique attributes, such as decentralization, enhanced security, and increased user control, set them apart from traditional applications. Dapps leverage blockchain technology to deliver innovative solutions that can operate independently of central authority, contributing to a paradigm where users have greater autonomy over their digital interactions.
The impact of dapps extends across various sectors, including finance, gaming, supply chain, and social media, among others. With their ability to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions and eliminate intermediaries, dapps are poised to redefine how industries conduct business. Furthermore, as the technology matures, we are likely to witness an increase in usability and accessibility, which will attract a broader audience, thus paving the way for mainstream adoption.
In light of this evolution, it becomes crucial for stakeholders—developers, businesses, and consumers alike—to remain informed about the advancements in decentralized technologies. The rapid growth of the dapp ecosystem suggests a continually changing environment, presenting both opportunities and challenges. By understanding the implications and potential of these applications, individuals and organizations can better position themselves in future endeavors, leveraging dapps to drive innovation and efficiency.
Ultimately, dapps have the potential to reshape the future of software development and influence the way we engage with technology in our daily lives. The call to action is clear: staying abreast of the developments in the realm of decentralized applications will enable one to harness their full potential and partake in this exciting technological revolution.






4 thoughts on “Understanding Decentralized Applications (DApps): The Future of Software Development”