Understanding Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing the Digital Era

Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology represents a revolutionary advancement in the digital landscape, providing a decentralized method for securely recording information. At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that enables multiple parties to maintain a shared database without relying on a central authority, thereby enhancing transparency and security. Each entry in this ledger is cryptographically secured and linked to the previous entry, forming a chain of blocks that cannot be altered retroactively without consensus from the network. This fundamental principle of immutability is one of the key aspects that make blockchain technology so valuable.
Table of Contents
The operational framework of blockchain technology revolves around several critical components, including nodes, mining, consensus protocols, and smart contracts. Nodes are individual computers that connect to the blockchain network and maintain a copy of the entire ledger. Mining is the process through which transactions are validated and added to the blockchain, typically through solving complex mathematical problems. Consensus protocols, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, are mechanisms that ensure agreement among nodes about the current state of the blockchain, preventing malicious actors from tampering with the data. Additionally, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the agreement directly written into code, facilitating automated transactions without intermediaries.
The significance of blockchain technology in today’s digital environment cannot be overstated. Its ability to provide a secure framework for digital transactions has transformative potential across various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. By increasing trust and efficiency, blockchain technology supports innovative applications such as cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). As we delve deeper into this technology in the subsequent sections, the various use cases and implications of blockchain will be explored, further illustrating its role in shaping the future of digital interactions.
The Key Components of Blockchain
Blockchain technology comprises several essential components that work in tandem to create a secure and decentralized digital ledger. Understanding these components is crucial for appreciating how blockchain operates and the roles they play within the system.
At the foundation of blockchain technology are blocks. Each block serves as a container for a set of transactions or records. When filled, the block becomes linked to the preceding block through a cryptographic hash, creating a chain. This mechanism ensures that altering any specific block would require changes to all subsequent blocks, thus maintaining an unalterable history of transactions. Each block typically contains a timestamp, a unique identifier, and the transaction data itself, which are crucial for maintaining transparency and accountability within the network.
Nodes refer to the individual participants in the blockchain network. Each node is a computer that holds a copy of the entire blockchain, contributing to the overall network’s resilience. There are different types of nodes, including full nodes, which validate transactions and maintain the entire blockchain, and light nodes, which only hold a part of the blockchain needed for reduced resource consumption. Nodes communicate with one another to propagate new transactions and blocks throughout the network, ensuring that all copies of the blockchain remain synchronized.
The role of miners is pivotal within the realm of blockchain technology. Miners are specialized nodes that validate transactions and create new blocks through a process known as mining. This involves solving complex mathematical problems to confirm the legitimacy of transactions. In return for their efforts, miners are often rewarded with cryptocurrency, incentivizing their participation in the network. The competition among miners also helps secure the network against manipulation and attacks, as the effort required to alter any block is substantial.
How Blockchain Works: A Simplified Explanation
Blockchain technology operates as a decentralized ledger system that records transactions across numerous computers, ensuring that the information is secure, transparent, and immutable. When an individual initiates a transaction, it is packaged into a block along with other transactions that occurred simultaneously. This block is then broadcast to all participants in the blockchain network.
Next, the transaction undergoes a validation process. Each participant, often referred to as a node, verifies the transaction based on predetermined criteria. This validation is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. If a majority of nodes agree that the transaction is valid, the block is added to the existing chain of blocks, hence the term “blockchain.” This process ensures that only legitimate transactions are recorded, reducing the risk of fraud.
Consensus mechanisms play a pivotal role in how blockchain technology maintains trust. Two of the most widely used mechanisms are proof of work (PoW) and proof of stake (PoS). Proof of work requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. This method, while secure, can be energy-intensive and time-consuming. Alternatively, proof of stake selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This process is often more energy-efficient and can allow for faster transaction validation.
Both methods aim to achieve the same ultimate goal: to secure the network and establish trust among participants. By decentralizing control and allowing multiple stakeholders to validate transactions, blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority, fostering a more democratic and transparent process within digital transactions. Understanding these fundamental principles illustrates how blockchain operates as a robust framework for secure digital interactions.
Types of Blockchain: Public vs. Private
Blockchain technology has evolved significantly, leading to the creation of various types, each serving specific purposes. The two primary types of blockchain systems are public and private blockchains, each with distinct features and use cases.
A public blockchain is a decentralized network that allows anyone to participate in the transaction verification process. This type of blockchain operates on a permissionless basis, meaning that participants can join freely without needing prior approval. One of the most notable examples of public blockchain technology is Bitcoin, which enables users to transfer currency without intermediaries. Public blockchains are typically transparent, immutable, and highly secure due to their distributed nature. They are particularly effective for applications that require trustless interactions among stakeholders, such as cryptocurrency transactions and decentralized applications (dApps).
In contrast, a private blockchain is a permissioned network where access is restricted to specific users. This type of blockchain technology is commonly deployed within organizations and enterprises that require enhanced privacy and control over their data. Private blockchains allow for greater scalability and efficiency since they can manage a limited number of nodes controlled by an authority. They are suitable for applications like supply chain management, where companies need to monitor and verify specific transactions without exposing sensitive information to the public. Furthermore, private blockchains can implement more complex consensus mechanisms, allowing for faster transaction times compared to their public counterparts.
There is also a hybrid option known as consortium blockchains, which merges elements of both public and private types. These systems allow multiple organizations to participate in the verification process while maintaining some level of privacy. Ultimately, the choice between public and private blockchain technology largely depends on the specific needs of an organization and the desired level of transparency and control.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
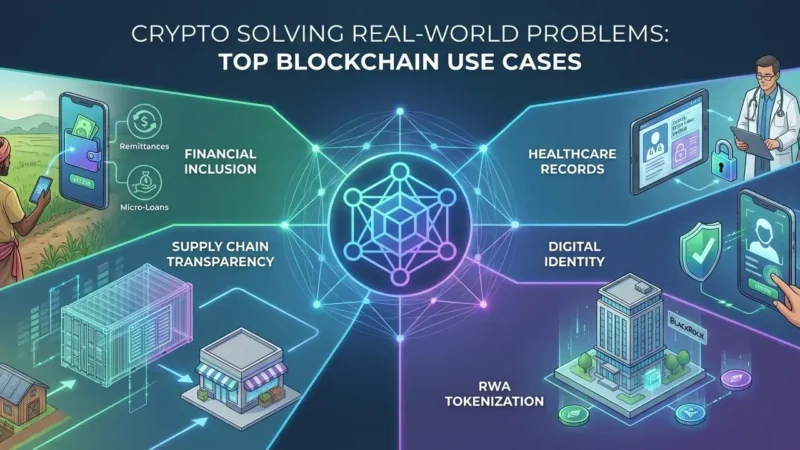
Blockchain technology has established itself as a transformative force across a multitude of industries. One of the most recognized areas is finance, where blockchain has enabled peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, thereby reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency. Major financial institutions, such as JPMorgan Chase, have adopted blockchain-based solutions for cross-border payments, showcasing the technology’s capability to facilitate quick and secure transactions.
In the healthcare sector, blockchain technology is being leveraged to enhance the security and interoperability of patient records. By creating a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger, healthcare providers can ensure that patient data is not only secure but also easily accessible to authorized individuals. This has the potential to improve patient outcomes through better data management and reduced errors. Organizations like MedRec are already implementing blockchain solutions to revolutionize how medical records are handled.
Supply chain management is another field experiencing significant benefits from blockchain technology. The ability to track products in real-time and verify the authenticity of goods at every stage of production and distribution enhances transparency and reduces the risk of fraud. Companies like IBM and Maersk have partnered to create blockchain networks that enable end-to-end visibility in supply chains, improving efficiency and trust among partners.
Digital identity management is rapidly evolving with the integration of blockchain technology. By providing individuals with control over their own data, blockchain offers a secure and decentralized method of verifying identity. This could eliminate identity theft and fraud, as well as streamline processes in various sectors. Startups like Civic are pioneering efforts to establish self-sovereign identities through blockchain solutions.
The diverse applications of blockchain underline its potential to revolutionize industries by improving transparency, security, and efficiency. As organizations continue to explore innovative implementations, the future of blockchain technology appears promising.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force across various sectors, providing numerous advantages that benefit both businesses and consumers alike. One of the foremost benefits is enhanced security. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that data is stored across a network of computers, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to tamper with the information. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous block through cryptographic hashes, which adds an additional layer of protection. This makes blockchain an appealing option for industries handling sensitive data, such as finance and healthcare.
Another significant advantage of blockchain technology lies in its transparency. Each transaction recorded on a blockchain is visible to all participants, allowing stakeholders to verify the authenticity of data. This unprecedented level of transparency can help build trust between consumers and businesses, as they can track the origin and movement of products or services in real-time. Such access to information not only reduces fraud but can also enhance corporate accountability.
Cost reduction is also a notable benefit of adopting blockchain technology. By eliminating intermediaries involved in traditional transaction processes, businesses can significantly lower operational costs. Blockchain facilitates smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules, thereby streamlining processes and reducing the time and resources typically required for transactions.
Finally, the increased efficiency that blockchain technology brings cannot be overstated. By automating and simplifying processes, businesses can significantly enhance their operational workflows. This efficiency is evident in various applications, from supply chain management to payment processing, demonstrating how blockchain can fundamentally improve organizational performance.
In conclusion, the adoption of blockchain technology presents numerous benefits including heightened security, improved transparency, cost savings, and enhanced efficiency. As more businesses and consumers recognize these advantages, the integration of blockchain into everyday operations is likely to become increasingly prevalent.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Despite its transformative potential, blockchain technology faces several significant challenges and limitations that cannot be overlooked. One of the primary concerns is scalability. Most blockchain networks experience considerable inefficiency in handling a high volume of transactions simultaneously. For instance, Bitcoin can process roughly seven transactions per second, while traditional payment systems like Visa can handle thousands per second. This discrepancy raises questions about the viability of blockchain for mass adoption in industries requiring fast and reliable transaction processing.
Another critical issue is energy consumption. The consensus mechanisms employed by many blockchain networks, particularly proof-of-work, demonstrate alarming energy requirements. According to some estimates, Bitcoin mining consumes as much energy annually as some entire countries. With growing environmental concerns, the ongoing reliance on energy-intensive algorithms raises questions about the long-term sustainability of widespread blockchain adoption.
Regulatory concerns further complicate the landscape of blockchain technology. Varying regulatory frameworks across countries lead to uncertainty within the ecosystem, deterring businesses from adopting blockchain solutions. For example, issues surrounding cryptocurrency usage, data privacy, and compliance with existing financial regulations create barriers that must be addressed for mainstream acceptance of blockchain applications.
Interoperability also presents a notable challenge. Different blockchain networks operate independently, making it difficult to share data and facilitate transactions across disparate platforms. This lack of compatibility not only hinders collaboration between different blockchain applications but also limits their effectiveness in solving real-world problems.
To overcome these hurdles, ongoing research and development efforts are necessary. Innovations such as sharding, proof-of-stake, and improved interoperability protocols show promise in enhancing the efficiency and practicality of blockchain technology. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in realizing the full potential of blockchain as a revolutionary force in the digital era.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends are set to shape its future. One of the most significant advancements is the increased focus on interoperability among various blockchain networks. Currently, numerous isolated blockchain systems operate independently, which can lead to inefficiencies and a lack of scalability. However, the development of cross-chain technology aims to create seamless interactions between different blockchain platforms, allowing for greater data transfer and communication. This interoperability is crucial for enhanced functionality and will likely facilitate the broader adoption of blockchain across industries.
In addition, the integration of blockchain technology with other revolutionary technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds substantial promise. IoT devices can benefit from blockchain’s inherent security features, creating trusted networks that protect sensitive data from potential breaches. For instance, by utilizing decentralized ledgers, businesses can track supply chains in real-time, ensuring authenticity and transparency while minimizing fraud. Coupling blockchain with AI also allows for more efficient data processing and decision-making, paving the way for intelligent contracts that automate various business operations.
Moreover, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging trend significantly influencing the future of blockchain technology. DeFi applications leverage blockchain to offer financial services without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or brokers. This democratization of finance empowers users by providing them with greater control over their assets and increasing access to financial services, especially in underserved markets. As the DeFi sector continues to grow, it is expected to drive innovation within the blockchain space, potentially resulting in new models for lending, insurance, and investment.
Stay informed, read the latest crypto news in real time!
Conclusion: The Impact of Blockchain on the Future
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the complexities and transformative potential of blockchain technology in various sectors. As a decentralized ledger that securely records transactions across networks, blockchain has demonstrated remarkable utility in industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more. These applications illustrate its capability to enhance transparency and reduce fraud by enabling immutable records that can be audited by all relevant parties.
The future impact of blockchain technology is likely to be profound, as organizations continue to recognize its benefits in promoting efficiency and trust. By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain offers the possibility of significant cost reductions and faster transaction times. Additionally, the integration of smart contracts—automated contracts written in code—further expands the reach of blockchain applications, allowing for complex agreements to be executed seamlessly without human intervention. This could redefine many traditional business practices and models.
Moreover, the push towards a decentralized future may democratize access to resources and services, providing underrepresented communities more opportunities to engage in economic activities. The adoption of blockchain can facilitate greater financial inclusion, giving individuals in remote areas access to banking services and secure transaction capabilities. Furthermore, sectors such as voting, identity verification, and data management stand to benefit tremendously from the robustness of blockchain technology, which can protect against fraud and unauthorised alterations.
In conclusion, the transformative impact of blockchain technology is undeniable as it continues to evolve and permeate various aspects of daily life and business operations. Its potential to create a more secure, transparent, and efficient world cannot be overstated, and the future holds promise for innovative applications that further leverage its unique attributes. As we move forward, embracing and adapting to blockchain technology will be essential for stakeholders across all sectors.






2 thoughts on “Understanding Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing the Digital Era”